Scientific Name:
Gleditsia triacanthos
Description:
Honey locusts, Gleditsia triacanthos, can reach a height of 20–30 m (66&–100 ft), with fast growth, and are relatively short-lived; their life spans are typically about 120 years, though some live up to 150 years. They are prone to losing large branches in windstorms. The leaves are pinnately compound on older trees but bipinnately compound on vigorous young trees. The leaflets are 1.5–2.5 cm (smaller on bipinnate leaves) and bright green. They turn yellow in the fall (autumn). Leafs out relatively late in spring, but generally slightly earlier than the black locust (Robinia pseudoacacia). The strongly scented cream-colored flowers appear in late spring, in clusters emerging from the base of the leaf axils.
The fruit of the honey locust is a flat legume (pod) that matures in early autumn. The pods are generally between 15–20 cm. The pulp on the insides of the pods is edible, unlike the black locust, which is toxic. The seeds are dispersed by grazing herbivores such as cattle and horses, which eat the pod pulp and excrete the seeds in droppings; the animal’s digestive system assists in breaking down the hard seed coat, making germination easier. In addition, the seeds are released in the host’s manure, providing fertilizer for them. Honey locust seed pods ripen in late spring and germinate rapidly when temperatures are warm enough.
Honey locusts commonly have thorns 3–10 cm long growing out of the branches, some reaching lengths over 20 cm; these may be single, or branched into several points, and commonly form dense clusters. The thorns are fairly soft and green when young, harden and turn red as they age, then fade to ash grey and turn brittle when mature. These thorns are thought to have evolved to protect the trees from browsing Pleistocene megafauna which may also have been involved in seed dispersal, but the size and spacing of them is useless in defending against smaller extant herbivores such as deer. In much of the Midwest, honey locust is considered a weed tree and a pest that establishes itself in farm fields. Thornless forms (Gleditsia triacanthos inermis) are occasionally found growing wild and are available as nursery plants.
Range and Habitat:
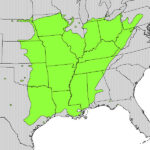
Honey locust is native to central North America. It is mostly found in the moist soil of river valleys ranging from southeastern South Dakota to New Orleans and central Texas, and as far east as eastern Massachusetts.
Uses:
Honey locusts produce a high quality, durable wood that polishes well, but the tree does not grow in sufficient numbers to support a bulk industry; however, a niche market exists for honey locust furniture. It is also used for posts and rails since it takes a long time to rot. In the past, the hard thorns of the younger trees have been used as nails.
Its cultivars are popular ornamental plants, especially in the northern plains of North America where few other trees can survive and prosper. It tolerates urban conditions, compacted soil, road salt, alkaline soil, heat and drought. The popularity is in part due to the fact that it transplants so easily. The fast growth rate and tolerance of poor site conditions make it valued in areas where shade is wanted quickly, such as new parks or housing developments, and in disturbed and reclaimed environments, such as mine tailings. It is resistant to gypsy moths but is defoliated by another pest, the mimosa webworm. Spider mites, cankers, and galls are a problem with some trees. Many cultivated varieties do not have thorns.
Despite its name, the honey locust is not a significant honey plant. The name derives from the sweet taste of the legume pulp, which was used for food by Native American people, and can also be fermented to make beer. The long pods, which eventually dry and ripen to brown or maroon, are surrounded in a tough, leathery skin that adheres very strongly to the pulp within. The pulp—bright green in unripe pods—is strongly sweet, crisp and succulent in unripe pods. Dark brown tannin-rich beans are found in slots within the pulp.
The honey locust is popular with permaculturalists across the globe, for its multiple uses. The legumes make a valuable, high protein cattle fodder, which becomes more readily accessible with the thornless (inermis) variety. The broad shade of the tree canopy is of great value for livestock in hotter climates, such as Australia. It is also claimed to be a nitrogen fixer, by way of rhizobium, which benefits the surrounding soil and plants. The durability and quality of the timber, as well as the ability to produce its own nails, fits the paradigm of self-sustaining agriculture that requires fewer external inputs/resources.
Ranchers and farmers, though, do deem this species as invasive because it quickly can move into pastures and grazing lands out-competing grasses for living space.
The tree has been used in traditional Native American medicine. Extracts of Gleditsia possess important pharmacological activities in treating rheumatoid arthritis, as anti-mutagenic, anticancer and have significant cytotoxic activity against different cell lines. Seeds of Gleditsia triacanthos contain a trypsin inhibitor.